If you are interested in ecology and recycling - sign up for our newsletter
Computer Disposal - What to Do with Worn-out Parts?
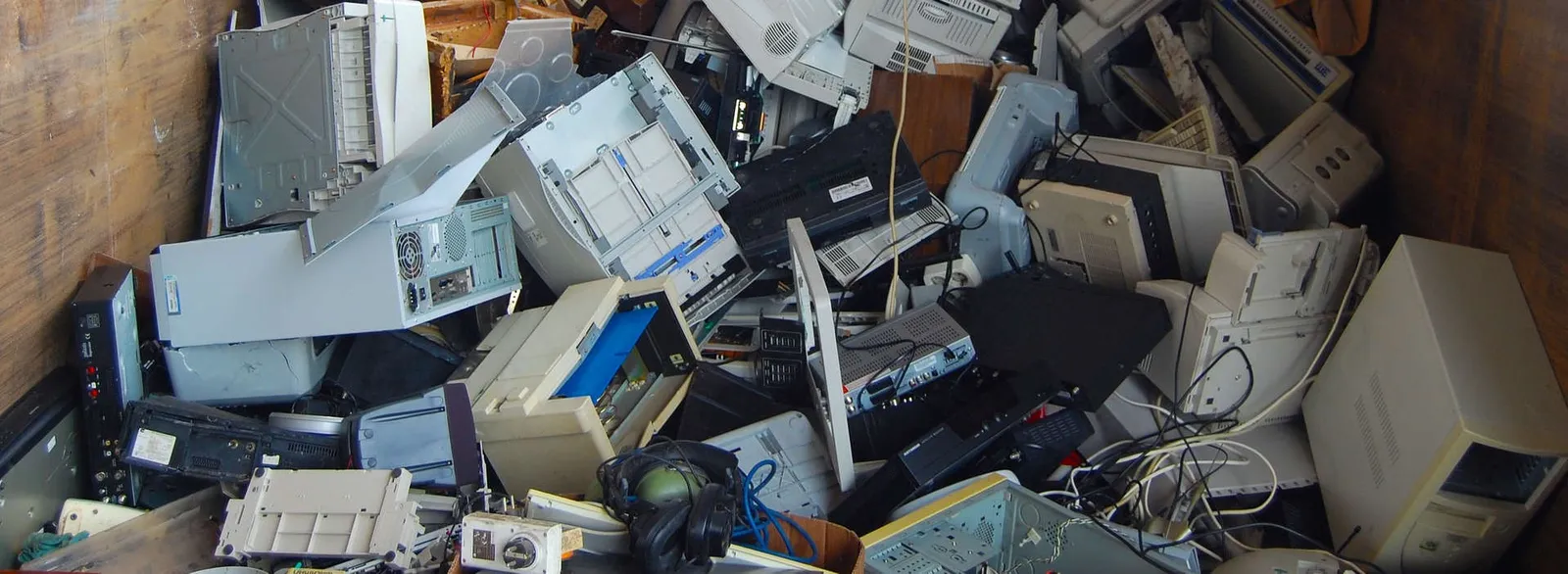
A computer consists of many technologically advanced components. Inside these parts are chemical compounds that can pose a threat to human health and the environment. When the equipment is new and functioning correctly, it does not pose a threat, but this changes over time – as years and usage take their toll, the device's properties deteriorate, and hazardous chemicals can escape from damaged or destroyed casings. A computer for disposal – that is, one that is damaged or completely destroyed and not working properly – should under no circumstances be stored with other waste, as it simply poses a risk that cannot be allowed. Therefore, such equipment should be taken to an appropriate place. According to the directive of the European Parliament, the disposal and recycling of a computer and its components must take place in professional and fully controlled conditions. Used equipment should therefore be handed over or sold at a suitable place, such as a professional IT equipment collection point.
What Does Computer Disposal and Recycling Entail?
Computer disposal is nothing more than safe dismantling and removal of harmful substances. Recycling, however, is more complicated. It's important to remember that not everything is subject to recycling. Components designated for reuse must meet certain conditions. Recycling involves dismantling the equipment so that as many of its elements as possible can be reused (without posing a danger). Components in good condition undergo repair and regeneration and are separated from the broken components. If the computer for disposal is in very poor condition, some materials, energy, or substances preserved in electronic waste are recovered.
Which Parts Are Subject to Recycling and Disposal?
According to the law, there are several groups of equipment that are subject to recycling, including:
- Monitors, screens, and devices with a screen area larger than 100cm2 (e.g., laptops);
- Small-sized equipment with dimensions not exceeding 50 cm (personal computers, printers, routers);
- Large-sized equipment with dimensions exceeding 50 cm (large computers and printers, copying equipment).
All computer parts can be subject to recycling if they are classified for it. Even from very damaged and worn-out equipment, materials like glass, plastics, metals, or energy can be recovered. Before handing over the equipment to a collection point, the hard drive should be cleared of stored data. Meanwhile, toxic substances are neutralized in special installations.