If you are interested in ecology and recycling - sign up for our newsletter
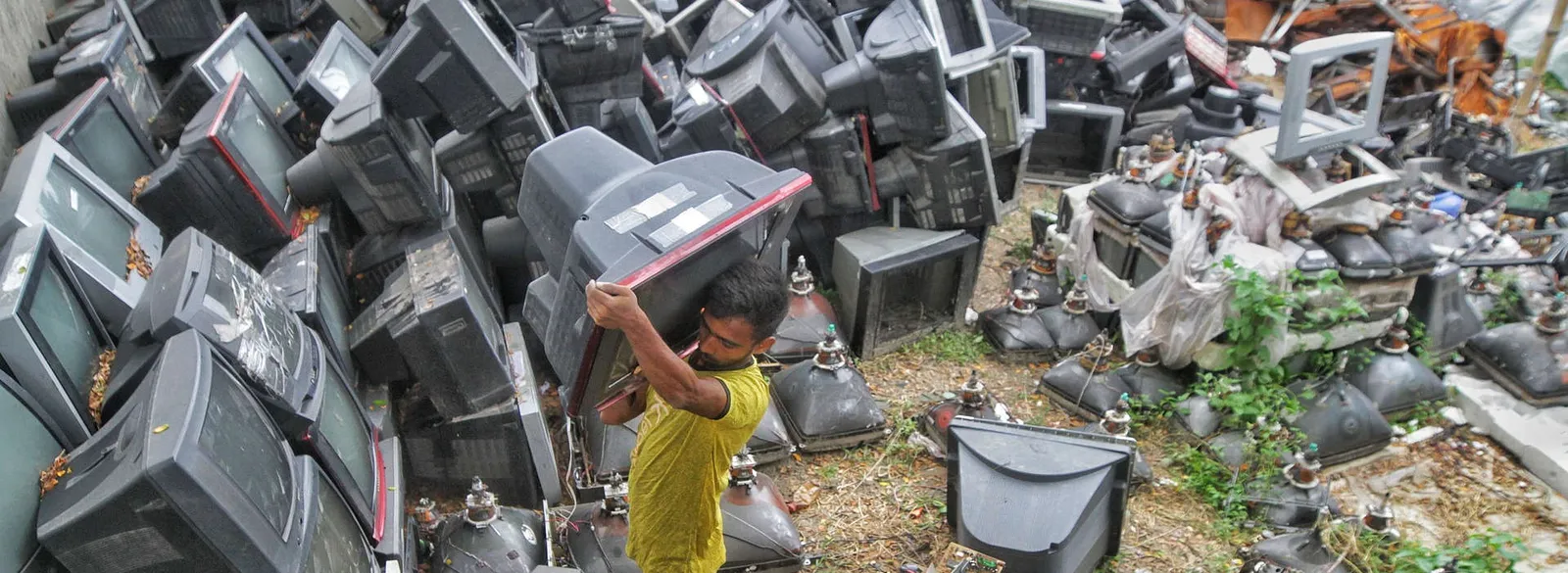
Electronic waste, or e-waste, includes all discarded electrical or electronic devices—ranging from smartphones and laptops to larger household appliances like refrigerators. E-waste is one of the fastest-growing types of waste globally, and understanding its impact on our environment is crucial for everyone. With technology advancing at a rapid pace, electronic products are being replaced more frequently, contributing to a significant increase in e-waste production. Without proper disposal and recycling, e-waste poses serious environmental and health hazards.
What Exactly is E-waste?
E-waste refers to any electronic device that is no longer wanted, either because it is broken or outdated. This can include everything from an old phone to a broken washing machine. Unlike regular waste, e-waste contains a mix of materials, including valuable metals like gold, silver, and copper, as well as hazardous substances that require careful disposal. Improper handling of these materials can have detrimental effects on the environment.
One of the challenges with e-waste is that it can be difficult to categorize. Items that might seem harmless, such as old remote controls or cables, actually contain components that require specialized processing to prevent environmental damage. Moreover, the rapid pace of innovation means that devices become obsolete quickly, leading to an ever-growing pile of discarded electronics.
Efforts to address e-waste start with understanding what it is and where it comes from. E-waste is generated by both individuals and businesses. For example, when companies upgrade their office equipment, it often results in a large volume of outdated devices. Additionally, consumer behavior plays a key role—many people choose to replace rather than repair electronics, which adds to the waste problem.
The average household contains around 80 electronic items, many of which could become e-waste if improperly disposed of. Even small devices like electric toothbrushes or digital watches count as e-waste when discarded.
Why is E-waste Harmful?
When e-waste is improperly disposed of, it often ends up in landfills, where harmful chemicals can leach into the ground and pollute the soil and water. Many electronic devices contain toxic substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium, which pose a significant risk to both the environment and human health. These substances can contaminate groundwater, affecting drinking water supplies and agricultural activities.
Lead, for instance, is found in many electronic circuit boards and is highly toxic if it enters the human body. It can cause developmental issues in children and negatively impact the nervous system. Similarly, mercury, found in items like fluorescent bulbs and certain types of batteries, can cause severe damage to the kidneys and brain. Cadmium, another common component of electronics, is known to cause lung and kidney damage if inhaled or ingested.
Another issue is the open burning of e-waste, which releases dangerous fumes into the atmosphere. This practice is common in areas where informal e-waste recycling takes place, particularly in developing countries. Burning e-waste releases pollutants such as dioxins and furans, which are linked to respiratory problems and even cancer. The improper handling of e-waste also has social implications, as many people who work in informal recycling sectors are exposed to these hazardous substances without proper protective equipment.
When electronics end up in a landfill, heavy metals can seep into nearby water supplies, making the water unsafe for drinking or irrigation. This can have long-term impacts on local communities and ecosystems.
The Importance of Recycling E-waste
Recycling e-waste is not only important for protecting the environment but also helps recover valuable resources like metals, glass, and plastics. Proper recycling reduces the need to mine raw materials, which can be both environmentally destructive and energy-intensive. Many electronic devices contain rare earth metals, which are difficult and costly to extract. By recycling these devices, we can conserve these materials and reduce the environmental footprint associated with mining.
For example, a typical smartphone contains small amounts of gold, copper, and silver. If we fail to recycle these devices, we lose the opportunity to recover these precious resources. The process of recycling involves dismantling the devices, separating the components, and processing them to extract reusable materials. Specialized facilities are required to handle the hazardous substances safely while recovering valuable materials effectively.
Many companies now have take-back programs, making it easier for consumers to dispose of their old devices responsibly. Some manufacturers even offer incentives, such as discounts on new products, to encourage customers to return their old electronics for recycling. Additionally, local governments often organize e-waste collection events to provide residents with safe disposal options.
Recycling 1 million laptops saves the energy equivalent to the electricity used by over 3,500 homes in a year. This highlights the significant energy savings that can be achieved through proper recycling practices.